Hazard Quotient Formula : Lecture Material Food Safety Budi Widianarko Unika Soegijapranata : The soil concentration will vary with each scenario location, and the soil consumption rate varies for children and
Hazard Quotient Formula : Lecture Material Food Safety Budi Widianarko Unika Soegijapranata : The soil concentration will vary with each scenario location, and the soil consumption rate varies for children and. Hazard quotient h q = actual serum level × u f serum level at pod, thus implying that hqs below 1 indicate an absence of risk for. 1.2 μg/m3 upper bound cancer risk 1 in 10 5: A health risk analysis based on the mean target hazard quotient (thq) yielded values <1 for all metals for average and maximal consumers. 12 μg/m3 upper bound cancer risk 1 in 10 4: A hazard quotient of 1 or lower means adverse noncancer effects are unlikely, and thus can be considered to have negligible hazard.
The agency for toxic substances and disease registry (atsdr) is an agency of the u.s. 120 μg/m3 based on us epa iris (october 2011) noncancer hazard quotient = 1: A hazard quotient is the ratio of an exposure estimate to the appropriate mrl, reference dose (rfd)/reference concentration (rfc), or guidance value. From wikipedia, the free encyclopedia a hazard quotient is the ratio of the potential exposure to a substance and the level at which no adverse effects are expected. 12 μg/m3 upper bound cancer risk 1 in 10 4:
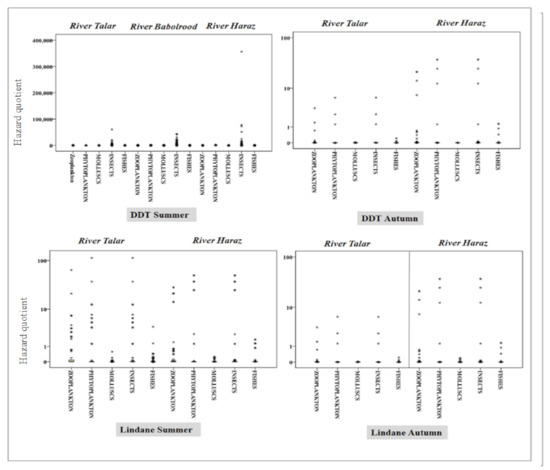
120 μg/m3 based on us epa iris (october 2011) noncancer hazard quotient = 1:
The total thq (tthq) which measures the aggregated risk due to heavy metal uptake via the ingestion of l. The ratio of the potential exposure to a substance and the level at which no adverse effects are expected (calculated as the exposure divided by the appropriate chronic or acute value). The agency for toxic substances and disease registry (atsdr) is an agency of the u.s. A hazard quotient of 1 or lower means adverse noncancer effects are unlikely, and thus can be considered to have negligible hazard. For a defined set of chemicals, the researchers explain that the hazard index for a target system is equal to the total sum of the individual chemical hazard quotients for each system; A health risk analysis based on the mean target hazard quotient (thq) yielded values <1 for all metals for average and maximal consumers. Mg/kg/day).a hazard index (hi) is the sum of hq's for all pathways and similar toxic effects.a hq of <0.2 for any given pathway is often considered acceptable; It can be seen from table 5 that most adults (both male and female) in yantai rural areas have taken in an excess of nitrate from the perspective of drinking water, and their hazard factor (hq) exceeds 1. Epa determines what hq level poses a concern to exposed individuals. Department of health and human services charged under the superfund act to assess the presence and nature of health hazards at specific superfund sites and to help prevent or reduce further exposure and the illnesses that result from such exposures. This assessment should include enough information that it can be evaluated by the epa, including a classification of the level of its hazard and a The estimated daily intake (edi), target hazard quotient (thq) and hazard index (hi) were calculated for infants between 0.5 and 5 y of age. It is primarily used by us epa to assess the ecological risk of pesticides.
The soil concentration will vary with each scenario location, and the soil consumption rate varies for children and Noncancer hazard quotient = 1: Hazard quotient • an alternative metric to the moe is the hazard quotient • individual risk is estimated by comparing the daily exposure with the rfd for each chemical of concern as expressed by the following equation: 2.1 μg/m3 upper bound cancer risk 1 in 10 6: From wikipedia, the free encyclopedia a hazard quotient is the ratio of the potential exposure to a substance and the level at which no adverse effects are expected.

If the quotient is less than 1, then the systemic effects are assumed not to be of concern;
The hazard quotients are added for the median exposure to get the hazard index for the median exposure. It is primarily used by us epa to assess the ecological risk of pesticides. 2.1 μg/m3 upper bound cancer risk 1 in 10 6: Noncancer hazard quotient = 1: The ratio is typically expressed as the measurable toxic exposure to a screening benchmark, such as the highest concentration of the toxicant known not to cause harm. If the quotient is less than 1, then the systemic effects are assumed not to be of concern; An hq greater than 1.0 is. Risk quotient = exposure / toxicity in above equation, exposure refers to estimated environmental concentration (eec). 120 μg/m3 based on us epa iris (october 2011) noncancer hazard quotient = 1: 12 μg/m3 upper bound cancer risk 1 in 10 4: The hazard quotient (hq) is the ratio of the exposure level at a site to the reference dose hq = site exposure (i.e., add) reference dose hazard quotient values are variable, with values less than and equal to 1 generally considered indicative of acceptable hazard. A hazard index is calculated for each exposure scenario of concern by first determining a hazard quotient for each of the mixture components. Hazard quotient • an alternative metric to the moe is the hazard quotient • individual risk is estimated by comparing the daily exposure with the rfd for each chemical of concern as expressed by the following equation:
This assessment should include enough information that it can be evaluated by the epa, including a classification of the level of its hazard and a The ratio of the potential exposure to a substance and the level at which no adverse effects are expected (calculated as the exposure divided by the appropriate chronic or acute value). A risk quotient (rq) is the ratio of a point estimate of exposure and a point estimate of effects. If the quotient is less than 1, then the systemic effects are assumed not to be of concern; If the hazard quotient is greater than 1, then the systemic effects are assumed to be of.

Since pod derived noael or bmd are based on animal experiments, the generally accepted default uf = 100 (i.e.
1.2 μg/m3 upper bound cancer risk 1 in 10 5: The respiratory quotient (or rq or respiratory coefficient), is a dimensionless number used in calculations of basal metabolic rate (bmr) when estimated from carbon dioxide production. The ratio of the potential exposure to a substance and the level at which no adverse effects are expected (calculated as the exposure divided by the appropriate chronic or acute value). Noncancer hazard quotient = 1: For purposes of preliminary quantitative risk assessment, exposures associated with a hq = 0.2. The soil concentration will vary with each scenario location, and the soil consumption rate varies for children and A health risk analysis based on the mean target hazard quotient (thq) yielded values <1 for all metals for average and maximal consumers. For a defined set of chemicals, the researchers explain that the hazard index for a target system is equal to the total sum of the individual chemical hazard quotients for each system; From wikipedia, the free encyclopedia a hazard quotient is the ratio of the potential exposure to a substance and the level at which no adverse effects are expected. The hazard quotient (hq) is further calculated using formula (4,5,6). Since pod derived noael or bmd are based on animal experiments, the generally accepted default uf = 100 (i.e. Human and ecological risk assessment: The estimated daily intake (edi), target hazard quotient (thq) and hazard index (hi) were calculated for infants between 0.5 and 5 y of age.
Komentar
Posting Komentar